In order to utilize AT&T LDAP (Active Directory) Plug-in to its fullest potential, we recommend administrators to understand the underlying architecture and principles of Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP).
Visualize a tree like structure and split into three Objects:
•Domain
•Organizational Unit
•Users
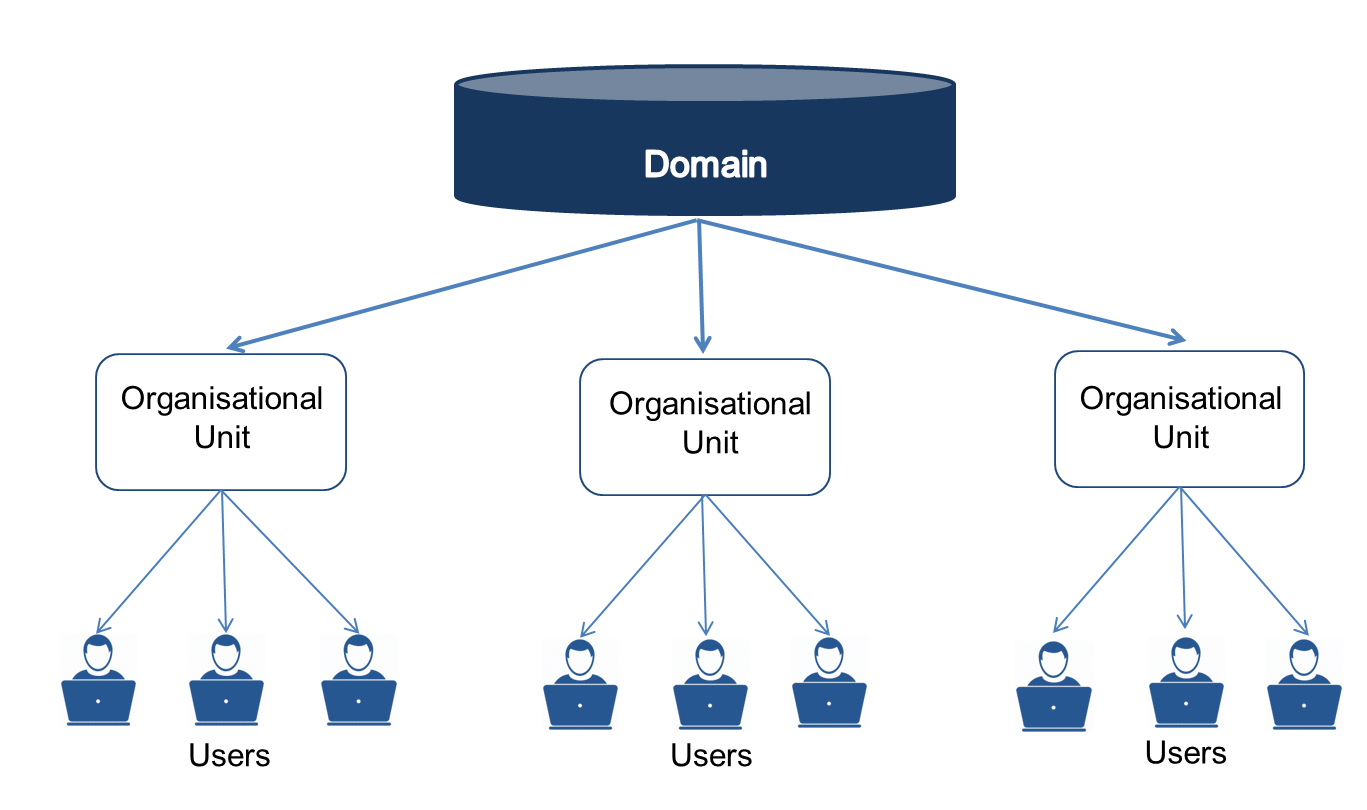
As depicted in the above diagram the objects – Domain, Organizational Unit & Users are in the form of a tree structure. Domain is the starting point of any sync operation and also known as Base DN. Other terminologies associated with an Active Directory structure are explained below:
Entries - Each of the objects listed above or if it is part of the Active Directory Structure are called entries. An entry is a collection of information about an entity which consists of three primary components:
•Distinguished name (DN)
•Collection of attributes
•Collection of object classes
DNs and RDNs - An entry's DN uniquely identifies that entry and its position in the directory information tree (DIT) hierarchy. DN comprises of zero or more elements called relative distinguished names or RDNs. Each RDN comprises of one or more (usually just one) attribute-value pairs.
Attributes – Attributes hold the data for an entry. Each attribute has an attribute type, zero or more attribute options, and a set of values that comprise the actual data.
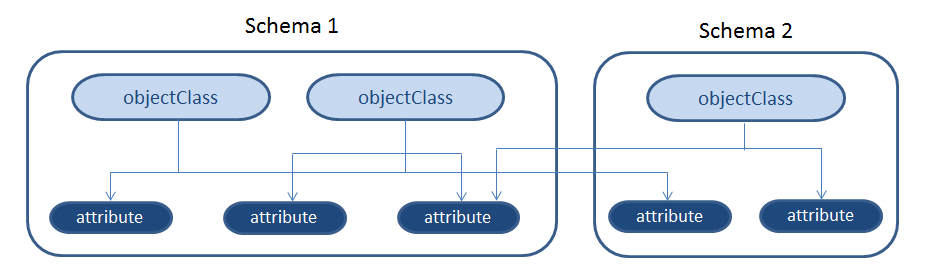
Object Classes - These are schema elements that specify collections of attribute types that may be related to a particular type of object, process, or other entity. Every entry has a structural object class, which indicates what kind of object an entry represents (e.g. whether it is information about a person, a group, a device, a service, etc.)
LDAP Schema - An LDAP schema is nothing more than a convenient packaging unit for containing broadly similar objectClasses and attributes.
The rule is that every attribute or objectClass, including its superior objectClass or attribute, used in an LDAP implementation must be defined in a schema, and that schema must be known to the LDAP server by a configuration procedure or option.
LDAP URL – LDAP URL encapsulates a number of pieces of information that may be used to reference a directory server, a specific entry in a directory server, or search criteria to identify matching entries within a directory server. Used for establishing connection.
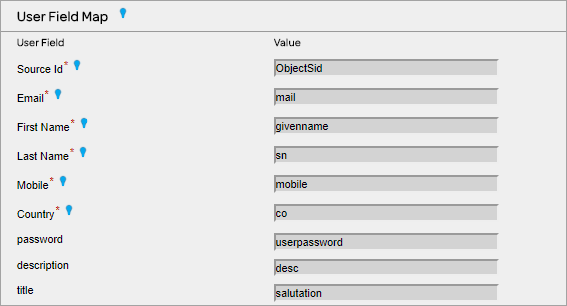
Object Mapping – LDAP (Active Directory) Plug-in for AT&T GSMS needs to identify and filter only those entries that represent ‘Customer’ entries and those that represent ‘User’ entries. In order to do this, the system provides a friendly way to map ‘ObjectClass’ attributes based on their associated value.
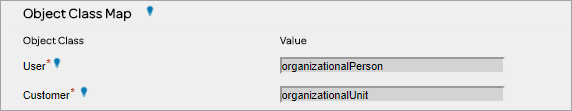
Customer Mapping – LDAP (Active Directory) Plug-in attributes are mapped to the Customer settings of GSMS. ‘DN’ will be used as the Customer ID and ‘OU’ attribute will be used as the Customer ‘Name’.
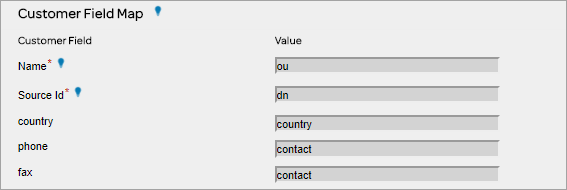
User Mapping – LDAP (Active Directory) Plug-in attributes are mapped to Customer settings for Users. Source ID Attribute will act as user’s ID. The mapping should be updated as below: